Arrhenius equation calculations involve using values for the variables to figure out how fast a reaction is. A is a term which includes factors like the frequency of collisions and their orientation.
The Pre Exponential Factor In The Arrhenius Equation Of A Second Order Reaction Has The Units
1

Estimation Of Power Transformer Remaining Life From Activation Energy And Pre Exponential Factor In The Arrhenius Equation Springerlink
E 272 Eulers number exponent.
Pre exponential factor. You may also find this called the pre-exponential factor. R is the universal gas constant. Where Z is the frequency factor frequency of collisions and is the steric factor deals with orientation of molecules.
52 Adapted from Ref. Calculate values of the activation energy and pre-exponential factor showing your working clearly. This equation can be used to understand how the rate of a chemical reaction depends on temperature.
Where k is the rate constant frequency of collisions resulting in a reaction. Pre-exponential factor Activation energy Gas constant Temperature R8314 Jmol-K NN Cl Cl N2 Benzene diazonium chloride Chlorobenzene rate constant k A exp. 109 11 - 1012 86.
Note that the preexponential factor is approximately IS. 1011 CH CH CH CH сн. In chemical kinetics the pre-exponential factor or A factor is the pre-exponential constant in the Arrhenius equation an empirical relationship between temperature and rate coefficientIt is usually designated by A when determined from experiment while Z is usually left for collision frequency.
A is the pre-exponential factorArrhenius originally considered A to be a temperature-independent constant for each chemical reaction. T is the absolute temperature in degrees Kelvin or Rankine. Consider an unburned mixture of propane with air which exists at a condition of 1 atm and 1500 K at 06 equivalence ratio.
Although often described as temperature independent it is actually dependent on temperature because it is related to molecular collision which is a function of temperature. Where A is the pre-exponential factor T is the temperature b is the temperature exponent E_a is the activation energy and R is the gas constant. -03 -03 01 01 1.
A pre-exponential factor sometimes called the Arrhenius constant in the same units as the rate constant. R universal gas constant equal to 8314 J K-1 mol-1. E a the activation energy of the reaction in J mol-1.
It is often taken as constant across small temperature ranges. The units of the pre-exponential factor A are identical to those of the rate constant and will. Calculate the frequency factor in chemical kinematics by understanding what the variables in the Arrhenius equation and manipulating them.
An Arrhenius equation example is given. This is because the reverse saturation current of the baseemitter PN junction is B B E B i E E E B B B S E i N W A qD n N W D N W D I A qn 2 2 since the. Comment on the effect of the reduction in ionic strength on the rate of reaction and determine whether the reactants which form the activated complex have charges of the same or different sign.
The pre-exponential factor is often represented by the following equation. R Universal gas constant. Table 1 summarizes for each transesterification reaction step the values used in this work of activation energy E a and pre-exponential factor k 0 of Arrhenius equation in the form k k 0 exp - E a RTThese kinetics follow a second-order mechanism for the forward and reverse reactions according to Vicente et al.
A is the pre-exponential factor and it is basically an experimentally-acquired constant correlating with collision frequency. Use collision theory to calculate an estimate of the Arrhenius pre-exponential factor in SI units for the reaction of. E_a is the activation energy in say J.
Now that we know E a the pre-exponential factor A which is the largest rate constant that the reaction can possibly have can be evaluated from any measure of the absolute rate constant of the reaction. The Pre-exponential Factor. The pre-exponential factor is also known as the frequency factor and represents the frequency of collisions between reactant molecules at a standard concentration.
T temperature in K. The frequency factor A. With the increase in the activation energy E a the rate constant K decreases and therefore the rate of reaction decreases.
E Activation energy in Jmol or KJmol. Knowledge of the excited state lifetime of a fluorophore is crucial for quantitative interpretations of numerous fluorescence measurements such as quenching polarization and FRET. The Arrhenius equation is mathbfk Ae-E_aRT where.
The Arrhenius equation is k Ae-EaRT where A is the frequency or pre-exponential factor and e-EaRT represents the fraction of collisions that have enough energy to overcome the activation barrier ie have energy greater than or equal to the activation energy Ea at temperature T. 反応モデルがアレニウス型Arrhenius equationで表され実験的に得られたアレニウスプロットがある場合にはその反応速度式の頻度因子 pre-exponential factorと見かけの活性化エネルギー activation energy を見積もることができますここで見かけと呼ぶのは実験結果で得られる反. It varies slightly with temperature although not much.
However more recent treatments include some temperature dependence - see Modified Arrhenius equation below. The value of A must be determined experimentally since it. The forward reaction rate is.
T Temperature in Kelvin. The n noted above is the order of the reaction. The pre-exponential factor p is mostly constant and invariant with ϕ s 1 - 0001 for the Poisson and the random beds 12 indicating that the probability of rays interacting with the particles is independent of the distance traveled by the rays within the bed for random distributions of particles.
K is the rate constant in units of 1M1 - m - ncdot s where m and n are the order of reactant A and B in the reaction respectively. E a RT lnk lnA E a RT We rearranged this equation to get the parameters appearing linearly and solved it using the normal equations. A Arrhenius factorpre-exponential factorfrequency factor.
Up to this point the pre-exponential term A in the Arrhenius equation Equation ref1 has been ignored because it is not directly involved in relating temperature and activation energy which is the main practical use of the equation. Lets solve this problem. 9 Fuel 11 Pre-exponential Factor A 1310 83.
With energy units in J we have R 8314472 JmolcdotK. Why might the experimental value of the Arrhenius pre-exponential factor be rather lower than that calculated. This theory helps explain how particles interact for a cause of the reaction and the formation of new productsThe Arrhenius equation significantly explains the effect of temperature on the reaction rate and hence the rate constant rmk.
54 x 10-4 M-1 s-1 A exp-160 x 10 5 Jmol8314 JK mol599K 54 x 10-4 M-1 s-1 1141x10-14 473 x 10 10 M-1 s-1. Fitting the dynamic magnetic data to the Arrhenius law gives the energy barrier ΔEk B 1095 K and pre-exponential factor τ 0 423 10 9 s under. Where I t is the intensity at time t α is a normalization term the pre-exponential factor and τ is the lifetime.
Image will be Uploaded Soon This is a graph of ln K. Find the value of the rate constant at 298 K. Oxidation of Hydrocarbons Tablo 51 Single-step reaction rate parameters for use with Egn.
A is the pre-exponential factor correlating with the number of properly-oriented collisions.

Solved Question No 3 A Use Collision Theory To Estimate Chegg Com

Some Thoughts And Or Questions About Activation Energy And Pre Exponential Factor Scientific Net
Two Reactions R1 And R2 Have Identical Pre Exponential Factors Activation Energy Of R1 Exceeds That Of R2 By 10kj Mol 1 If K1 And K2 Are Rate Constants For Reactions R1

The Pre Exponential Factor In The Arrhenius Equation Of A Second Order Reaction Has The Unit Youtube
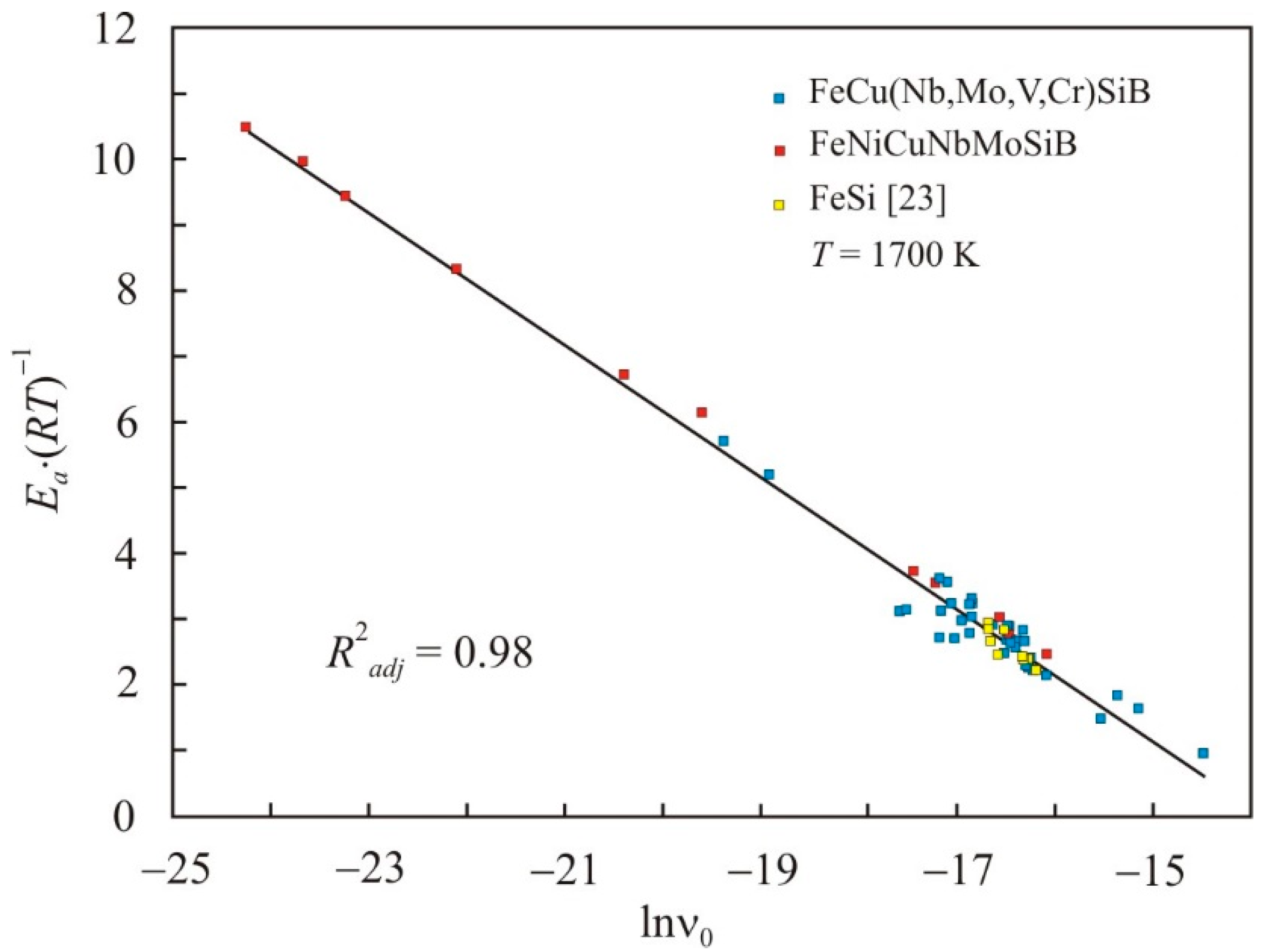
Nanomaterials Free Full Text Kinematic Viscosity Ofmulticomponent Fecunbsib Basedmelts Html

Calculation Of Pre Exponential Factor For Ethanol Air Single Step Download Table
Methodology For Calculating The Pre Exponential Factor Using The Isoconversional Principle For The Numerical Simulation Of The Air Injection Process

In Arrhenius Equation For Activation Energy K Ae E A Rt A Represents The Following 1 Pre Exponential Factor 2 Frequency Factor 3 Arrhenius Factor 4 Collision Factor And Frequency The Correct Anwer Is

